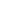
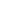When choosing a water pump, you may wonder about the differences between a vertical long-shaft pump and a submersible pump. These two types of pumps are classified differently and serve distinct applications.
Vertical long-shaft pumps are designed for applications requiring deep water extraction. These pumps extend downward from the installation point, with the motor positioned above the surface and the pumping components submerged. Their structure allows them to operate efficiently in environments such as offshore platforms, rivers, and deep wells. They often feature a multi-stage design, allowing them to generate higher pressure and lift water from significant depths.

A common characteristic of these pumps is the use of a one-stage double-suction design, which enhances water intake capacity. Since the motor remains above the water surface, maintenance and inspections are more accessible compared to fully submerged systems.
Submersible pumps, on the other hand, are fully submerged in the medium they are pumping. Their motor and pump components are encased in a sealed housing, preventing water ingress and ensuring safe underwater operation. These pumps are commonly used for applications such as wastewater treatment, drainage, and groundwater extraction.
Since submersible pumps operate below the water surface, they do not require long shafts or external support structures. This makes them more compact and easier to install in confined spaces. They also reduce the risk of cavitation, a common issue in pumps that operate with high suction lifts.
Pumps are categorized based on their operational design and working position. Submersible pumps are generally divided into standard submersible pumps and long-shaft submersible pumps. Vertical pumps, including high-speed pumps and barrel pumps, are classified based on their structural design. Some long-shaft submersible pumps belong to both categories, illustrating the overlap between these classifications.
Both vertical long-shaft pumps and submersible pumps require considerations regarding performance and maintenance.
Vertical Long-Shaft Pumps: These pumps may require periodic maintenance due to the extended shaft and bearings. Since the motor remains above the surface, it is easier to inspect and repair. However, vibrations caused by the long shaft can pilot operational challenges, requiring stable installation and careful alignment.
Submersible Pumps: These pumps are designed for direct immersion in the fluid, reducing the risk of leakage. Since they operate within the liquid, cooling is more efficient. However, maintenance can be more complex because the entire unit must be lifted from the medium for repairs or servicing.
Selecting between a vertical long-shaft pump and a submersible pump depends on factors such as application depth, space availability, and maintenance requirements.
If the installation site requires deep water access and the pump needs to be inspected frequently, a vertical long-shaft pump may be a suitable choice.
If compact installation and small surface infrastructure are priorities, a submersible pump may be a better fit.
Both types of pumps serve essential roles in various industries, from water supply systems to industrial fluid handling. Understanding their characteristics ensures an informed decision based on operational needs.
As a manufacturer of long-shaft pumps, we offer a variety of options tailored to different applications. By assessing specific requirements, you can select a pump that aligns with your operational needs and ensures efficient performance.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى