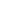
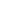Sewage pumps play a crucial role in wastewater management by transporting wastewater from one point to another, whether from homes, industries, or treatment facilities. Three common types of sewage pumps are above-ground sewage pumps, underground sewage pumps, and high-pressure sewage pumps. Each of these pumps is designed to meet specific needs, depending on the environment, the amount of wastewater to be moved, and the pressure requirements.
Above-ground sewage pumps are typically used for situations where wastewater needs to be transferred from a building or structure to a sewer system or a treatment plant. These pumps are positioned above ground, making them easier to install, maintain, and inspect. They are often used in residential and light commercial applications where space or the need for a submersible pump is not required.

These pumps are generally used in systems where wastewater is gravity-fed to the pump, and the pump is responsible for moving the water to a higher elevation or across a distance. The above-ground design allows for easy access to components like the motor and impeller for maintenance and repairs, which can reduce downtime and ensure long-term reliability.
Underground sewage pumps, also known as submersible pumps, are designed to operate while submerged in water. These pumps are typically installed in a sewage pit or sump, where they remain hidden below ground. Unlike above-ground pumps, which are exposed to the air, underground sewage pumps are submerged in the wastewater they are tasked with moving, offering greater protection from environmental factors such as weather or debris.
One key advantage of underground sewage pumps is their ability to operate quietly and efficiently. Because they are submerged, they are generally less prone to wear and tear from external elements. These pumps are often used in both residential and industrial settings where space is limited or aesthetics are a consideration, as the pump is hidden from view. They are typically used to pump wastewater from basements, sewage tanks, or septic systems to a treatment facility or municipal sewer system.
These pumps are designed to handle wastewater with various contents, including solid waste, which is why they are often equipped with grinding or cutting mechanisms. This allows them to break down solids before pumping them, ensuring smooth operation and reducing the risk of clogs in the system.
High-pressure sewage pumps are designed for situations where wastewater needs to be moved over long distances or to higher elevations. These pumps generate higher pressure levels than standard sewage pumps, making them ideal for industrial applications, large-scale wastewater treatment facilities, or systems with multiple levels.
High-pressure pumps are equipped with a more powerful motor and a robust impeller system, enabling them to generate the necessary pressure to move wastewater over longer distances or through complex pipe systems. These pumps are often used in large commercial or industrial environments where sewage must be pumped from lower levels to treatment plants or municipal systems.
One of the main advantages of high-pressure sewage pumps is their ability to overcome resistance from long pipelines or uphill pumping. They are especially useful in situations where gravity alone cannot move the wastewater efficiently. High-pressure sewage pumps are built with heavy-duty components to withstand the intense forces generated during operation, ensuring their durability and reliability over time.
Each type of above-ground, underground, and high-pressure sewage pump is suited for different applications, depending on the specific needs of the wastewater management system. Above-ground sewage pumps are ideal for easy installation and maintenance, underground sewage pumps are good for confined spaces and quieter operation, and high-pressure sewage pumps are essential for transporting wastewater over long distances or uphill.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى