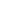
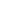Small dirty water submersible pumps are versatile units designed for handling contaminated liquids in space-limited applications. These compact pumps feature fully submersible designs with durable construction to process water containing small solids, sand, and mild debris.
A small dirty water submersible pump is designed to efficiently pump water that contains impurities, debris, or small particles. Their submersible design allows them to be placed directly in the water, offering easy operation without the need for suction lines.
Their submerged operation eliminates priming needs while reducing noise. These pumps offer plug-and-play simplicity with easy maintenance, making them ideal for temporary or permanent installations where space is limited but reliable wastewater removal is required.
The growing need for efficient wastewater handling in confined spaces has led to increased demand for small submersible pumps designed for dirty water applications. These compact yet powerful units provide reliable performance in challenging environments where space constraints and difficult fluids present operational challenges.

Modern small submersible pumps for dirty water incorporate several key design elements:
Compact footprints allow installation in tight spaces
Corrosion-resistant materials for extended service life
Robust impeller designs capable of handling solids and fibrous materials
Efficient motor technology small energy consumption
These pumps typically process water containing suspended solids up to specific size limitations, making them suitable for various contaminated liquid transfer applications. Their submersible nature eliminates priming issues while reducing noise during operation.
The adaptability of these pumps makes them valuable for multiple sectors:
Construction Sites - Effective dewatering of excavations and trenches
Municipal Maintenance - Clearing flooded basements and underground spaces
Agricultural Operations - Handling nutrient-rich wastewater in livestock areas
Industrial Facilities - Managing process water and mild effluent streams
Their portability allows for quick deployment in emergency situations, while durable construction ensures performance in demanding conditions. Many models feature built-in thermal protection and automatic shut-off systems to prevent damage during dry running conditions.
Compared to traditional centrifugal pumps, these compact submersible units offer distinct benefits:
Simplified installation without requiring dedicated pump houses
Reduced maintenance needs due to fewer external components
Improved safety with submerged operation of electrical hazards
Recent technological improvements have enhanced their capabilities:
Advanced seal systems prevent fluid ingress
Improved cooling mechanisms for continuous operation
Smart monitoring options in some premium models
Selection Considerations for good Performance
When choosing these pumps, operators should evaluate:
Required flow rates and head pressure
big solids handling capacity
Chemical compatibility with pumped fluids
Available power supply options
Required duty cycle and runtime
Proper sizing ensures efficient operation while preventing premature wear. Regular maintenance, including seal inspections and impeller cleaning, helps big service intervals.
Industry trends indicate growing interest in:
Enhanced materials for improved abrasion resistance
Integrated monitoring systems for predictive maintenance
More efficient motor designs reduce energy consumption
Modular configurations allow for easy field servicing
These innovations aim to further increase reliability while reducing the total cost of ownership for end users.
Small submersible dirty water pumps represent an effective solution for various liquid transfer challenges. Their combination of compact dimensions, solids-handling capability, and reliable performance makes them particularly valuable where space limitations exist.
With proper selection and maintenance, these pumps provide cost-effective performance in handling contaminated liquids, contributing to more efficient water management practices in industrial, commercial, and municipal applications. Their versatility and improving technology position them as essential tools for modern wastewater handling requirements.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى